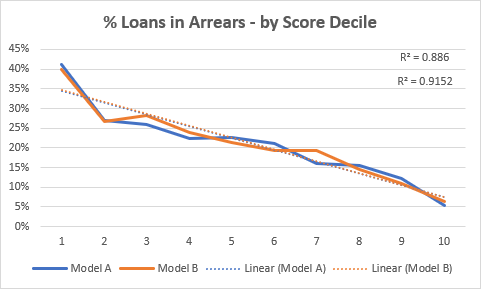
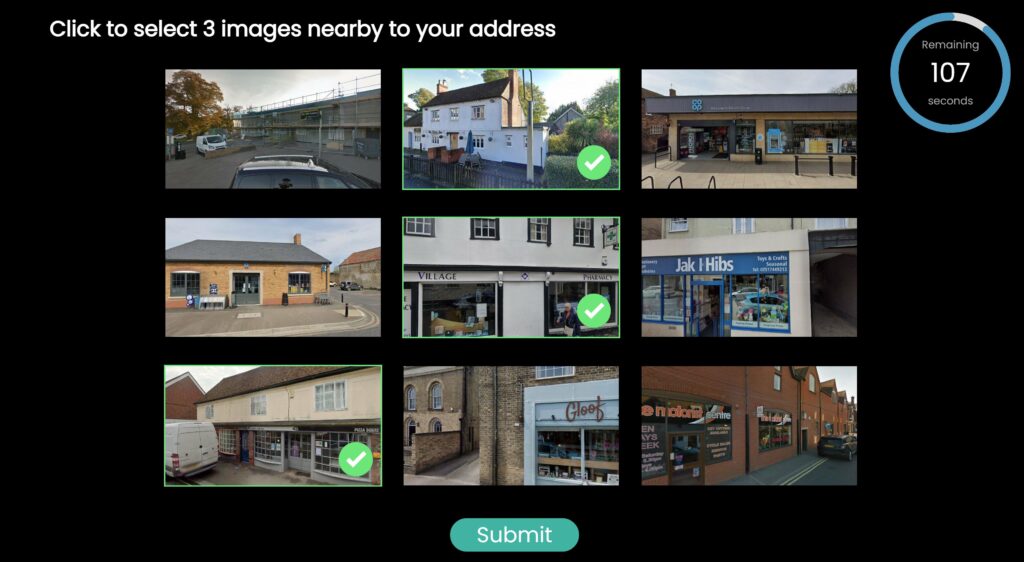
Our reliance on mobile devices for security purposes, like two-factor authentication (2FA), has given rise to a new form of cybercrime known as a SIM swap attack.
What is a SIM Swap Attack?
A SIM swap attack, also known as SIM splitting, simjacking, or SIM porting, is a type of fraud that involves a criminal tricking a mobile carrier into switching a phone number to a SIM card controlled by the criminal. Once successful, the attacker gains control over all calls, messages, and potentially, secure accounts linked to that phone number.
How Does a SIM Swap Attack Happen?
The process typically involves:
- Gathering Information: Fraudsters collect personal information about their target through phishing attacks, social engineering, or public databases.
- Impersonation: Armed with this information, the attacker contacts the victim’s mobile carrier, pretending to be the legitimate account holder.
- Deception: They then claim that their phone has been lost or damaged and request that the phone number be transferred to a new SIM card, which is in the possession of the fraudster.
- Switching SIMs: If the mobile carrier is convinced, they deactivate the victim’s SIM card and activate the new one. The attacker now receives all communications intended for the victim.
Motivations Behind SIM Swap Attacks
Fraudsters engage in SIM swap attacks primarily to:
- Hijack Accounts: Once they control the phone number, attackers can bypass 2FA systems, access victims’ personal and financial accounts, and reset passwords.
- Financial Gain: They often target bank accounts, cryptocurrency wallets, and other financial services to transfer funds illegally.
- Identity Theft: The attack can be a step towards more extensive identity theft operations.
The Vulnerability of SMS OTPs
One of the key reasons why SIM swap attacks are so effective is the vulnerability of SMS-based One-Time Passwords (OTPs) in 2FA systems:
- Single Point of Failure: If the phone number is compromised, all security relying on SMS OTPs falls apart.
- Carrier Dependence: The security of SMS OTPs depends on mobile carriers, who may not always have stringent verification processes.
- Delayed Detection: Victims often realize they’ve been attacked only after losing access to their services or noticing unauthorized activities.
SIM swap attacks represent a significant vulnerability in our current reliance on mobile-based security, particularly SMS OTPs for 2FA. They highlight the need for more secure forms of verification and authentication methods that do not rely solely on a phone number. Awareness, improved security protocols by carriers, and alternative 2FA methods can help mitigate the risks associated with these attacks. As technology evolves, so do the tactics of cybercriminals, making constant vigilance and adaptation a necessity in the digital world.
How can Honey Badger help?
Honey Badger provides real-time lookups against mobile network operators to identify recent SIM swaps. This instant and frictionless lookup will highlight risk of a SIM swap attack due to a number recently being ported. To find out more visit Honey Badger’s Risk Insights page.
Honey Badger also provides a more secure alternative to SMS OTP known as Silent Authentication+. This approach uses SIM based cryptography to prove a user is in possession of their trusted device. To find out more visit Honey Badger’s Silent Authentication+ page.